|
Armadillos | Armadillo Overview | Armadillo Damage Assessment | Armadillo Damage Management | Armadillo Resources | Armadillo Acknowledgments | ICWDM | Wildlife Species Information |
Damage Prevention and Control Methods
Exclusion

Armadillos have the ability to climb and burrow. Fencing or barriers, however, may exclude armadillos under certain conditions. A fence slanted outward at a 40o angle, with a portion buried, can be effective. The cost of exclusion should be compared to other forms of control and the value of the resources being protected.
Cultural Methods
Armadillos prefer to have their burrows in areas that have cover, so the removal of brush or other such cover will discourage them from becoming established.
Repellents
None are currently registered or known to be effective.
Toxicants
None are currently registered.
Fumigants
None are currently registered.
Trapping
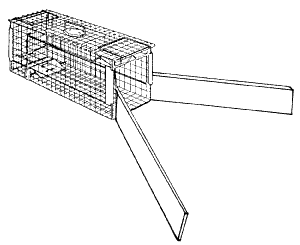
Armadillos can be captured in 10 x 12 x 32-inch (25 x 30.5 x 81-cm) live or box traps, such as Havahart, Tomahawk, or homemade types. The best locations to set traps are along pathways to armadillo burrows and along fences or other barriers where the animals may travel.
The best trap is the type that can be opened at both ends. Its effectiveness can be enhanced by using “wings” of 1 x 4-inch (2.5 x 10-cm) or 1 x 6-inch (2.5 x 15-cm) boards about 6 feet (1.8 m) long to funnel the target animal into the trap (Fig. 3). This set does not need baiting. If bait is desired, use overripe or spoiled fruit. Other suggested baits are fetid meats or mealworms.
Other traps that may be used are leghold (No. 1 or 2) or size 220 Conibear® traps. These traps should be placed at the entrance of a burrow to improve selectivity. Care should be taken when placing leghold traps to avoid areas used by nontarget animals.
Shooting
Shooting is an effective and selective method. The best time to shoot is during twilight hours or at night by spotlight when armadillos are active. A shotgun (No. 4 to BB-size shot) or rifle (.22 or other small caliber) can be used. Good judgment must be used in determining where it is safe to shoot. Check local laws and ordinances before using shooting as a control method.
Other Methods
Since most of the damage armadillos cause is a result of their rooting for insects and other invertebrates in the soil, soil insecticides may be used to remove this food source and make areas less attractive to armadillos.
|
Armadillos | Armadillo Overview | Armadillo Damage Assessment | Armadillo Damage Management | Armadillo Resources | Armadillo Acknowledgments | ICWDM | Wildlife Species Information |
Summary of Damage Prevention and Control Methods
Exclusion
Fences or barriers are generally not practical, but a possible option.
Cultural Methods
Clear brush and other cover to reduce available habitat.
Repellents
None are registered.
Toxicants
None are registered.
Fumigants
None are registered.
Trapping
Live traps (box traps). Leg hold traps (size No. 1 or 2). Conibear® 220.
Shooting
One of the most commonly used methods.
Other Methods
Soil insecticides that remove food sources will discourage armadillos from feeding in an area.
